
Human heart is a muscular organ which pumps blood into body day and night. It is one of the first organ to become functional in a foetus i.e. when we were in our mother’s womb. It continues to work till we are alive. The most important function of the heart is to supply oxygen and other nutrients to all organs.
Structure of heart:
It has 4 chambers. The proximal 2 chambers are called: 1)Right atrium and 2) left atrium and distal 2 chambers are 3)right ventricle and 4)left ventricles.
It has 4 valves which help to streamline blood from one chamber to another and prevent backward flow. They allow only one way flow.
- tricuspid valve which separates right atrium from right ventricle
- Mitral valve between left atrium and left ventricle
- pulmonary valve between right ventricle and pulmonary artery
- Aortic valve between left ventricle and aorta
It has 2 partitions which prevents intermixing of blood between right and lift sides.
- Inter atrial septum : separated right atrium from left atrium.
- Inter ventricular septum: separates right ventricle from left ventricle.
Circulation of blood in body, heart and lungs:
- As we work, oxygen in blood is utilised and carbon-di-oxide is produced. Veins carry this impure blood from body to right side of heart. Blood from head and hands is brought by superior vena cava and from legs and abdomen by inferior vena cava. It is collected into right atrium.
- Blood from right atrium goes to right ventricle through tricuspid valve.
- Right ventricle pumps this impure blood into pulmonary artery through pulmonary valve.
- Pulmonary artery carries it to lungs for purification. As there are 2 lungs, pulmonary artery has 2 branches right and left.
- Alveoli are the smallest working unit of lung where impure blood is brought in close vicinity of air. Carbon-di-oxide is released into air and oxygen is captured by haemoglobin in blood. Now blood is almost 100% saturated with oxygen. As we breathe we exhale carbon-di-oxide and inhale oxygen and maintain oxygen rich air in alveoli.
- Four pulmonary veins returns pure oxygenated blood to left atrium.
- It drains into left ventricle through mitral valve.
- Left ventricle forcefully ejects blood into aorta through aortic valve.
- Aorta caries blood to all tissues of body from head to toe.
This is how blood is circulated in body.
How our heart is controlled ?
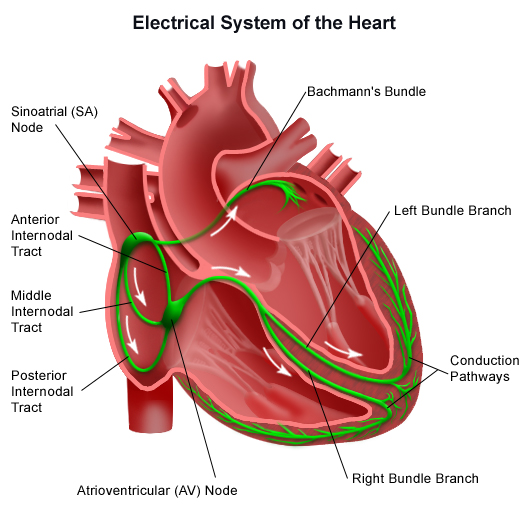
Our heart activity is controlled by electric impulse generated in sino atrial node. It is situated in right atrium close to superior vena cava and works as a natural pacemaker for heart. This impulse is carried to ventricles via small connection called Atrioventricular node. Specialised system of His bundle and Purkinje’s fibre spread it rapidly over ventricles. With every impulse, atria and ventricles contract in sequential manner to pump blood. After some time they relax again to receive more blood. This one cycle of contraction and relaxation makes a heart beat.
Heart beats at variable rate depending upon need of body. In a child, the rate is about 120 to 150/min and in an adult it is about 60 to 100/min. As we exercise, the rate increases. This will pump more blood into circulation.
Blood supply of heart:
Like every organ in body, heart also gets its blood supply from 2 coronary arteries called as right and left coronary arteries. They originate just above aortic valve, the first pair of arteries to originate from aorta. As per their names, they supply right and left side of heart but there variations are common.
How to maintain health of heart ?
Following are few tips to maintain a healthy heart
- Daily exercise for 40 mins for most days of week.
- Curtail intake of sugar, salt, fried and fatty food.
- Maintain ideal body weight
- Total abstinence from tobacco in any form, ethanol.
- Check blood sugar and lipid profile from age of 25 years and onwards.
