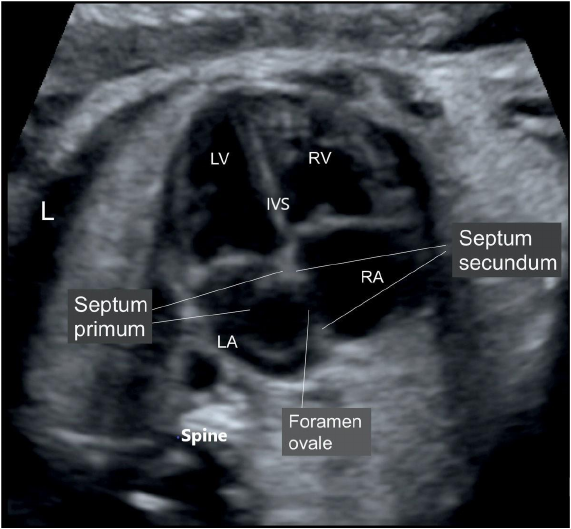
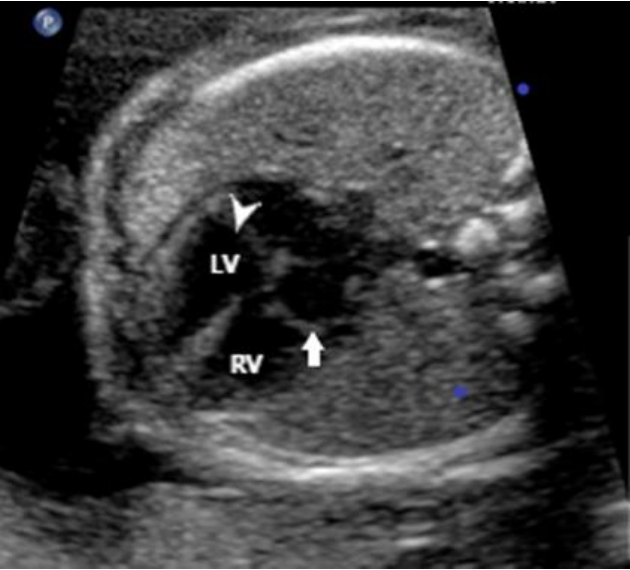
- 4 chamber view: most easily obtained.
- Anomalies detected in this view are generally major
- Anomalies of outflow tract may not be appreciated.
Basic definitions
- Mitral valve: More cranial, no septal attachment, bi-leaflet
- Tricuspid valve: More apical, septal attachment, tri-leaflet
- Left ventricle: Smooth wall, no apical trabeculations, no moderator band.
- Right ventricle: Rough wall, moderator band
4 chamber view
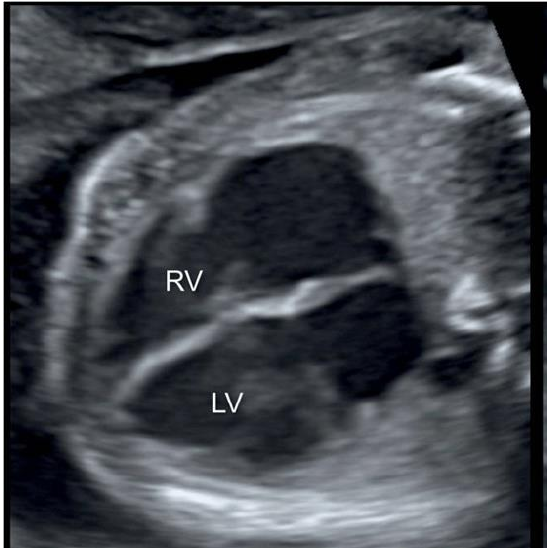
- LV Left ventricle
- RV Right ventricle
- LA Left atrium
- RA right atrium
- IVS inter ventricular septum
- L: Left side

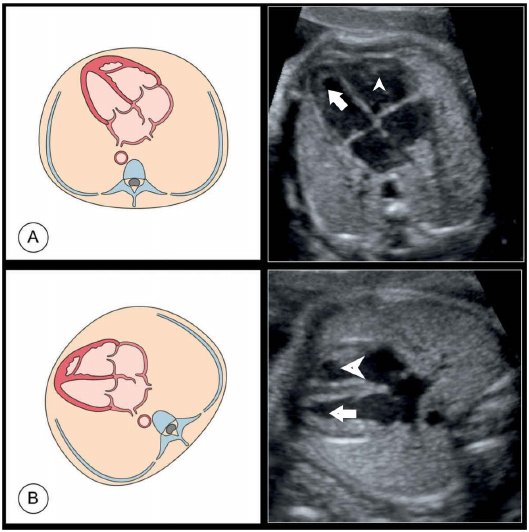
Arrow head:
Moderator band and
trabeculation of right
ventricle
Arrow: Smooth walled
left ventricle
Situs solitus, levocardia
- Left atrium: close to spine/ posterior, left sided, receives pulmonary veins
- Right atrium: Anterior , receive systemic venous drainage , rightward
- Left ventricle: More posterior and leftward
- Right ventricle: retro sternal, rightward
Analyzing 4 chamber view
Cardiac defects can have variety of morphology.
- 4 chamber heart
- Not 4 chambered heart/ small ventricle/ absent or hypoplastic Av valve
- Not so normal 4 chambered heart
- Lesions not seen on 4 chamber view
Anomalies diagnosed on 4 chamber view
- 4 chambered heart
- Ostium primum defect
- Complete AV canal defect
- Large VSD
- Ebstein Anomaly
- Congenitally corrected trans position of great arteries
- Cardiac masses
- Fetal arrhythmias
- Cardiomyopathy: Dilated / hypertrophic
- Pericardial effusion
- Not 4 chambered heart
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome ( some verities)
- Hypoplastic right ventricle ( some varities)
- Univentricular heart
- Double inlet ventricle,
- mitral atresia,
- tricuspid atresia
A not so normal 4 chamber view
- Endomyocardial fibroelastosis
- Aortic stenosis/ HLHS etc
- Discrepancies in sizes of ventricles and AV valves
- Coarctation
- Hypoplastic mitral valve/Varieties of HLHS,
- Hypoplastic tricuspid valve/ Hypoplastic RV
- Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Anomalies may NOT be suspected on
apical 4 chamber view
These are mainly conotruncal anomalie
- Aortic stenosis
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Coarctation of aorta
- Truncus arteriosus
- Double outlet right ventricle
- Pulmonary atresia
- List is not exhaustive
Anomalies seen on 4 chamber view
with 4 chambered heart
- All 4 chambers are well formed.
- Most defects are amenable to good surgical repair or palliation.
- Most conotruncal anomalies like TOF/ TGA/ DORV can have a normal 4 chamber view.
Ostium primum ASD
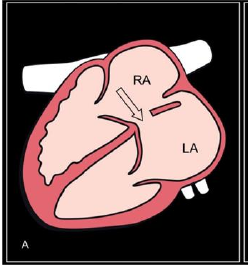
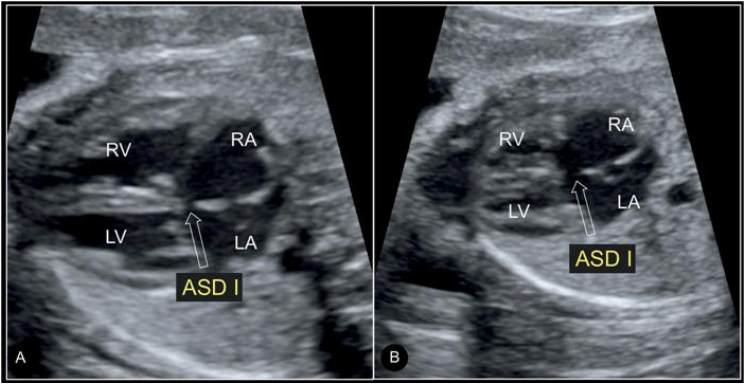
Ostium primum ASD Salient feature
- Absent septum primum at its normal position
- Both AV valves are at same level
- Regurgitation of Rt and/or left AV valve
- No defect on ventricular side
Complete AV canal defect
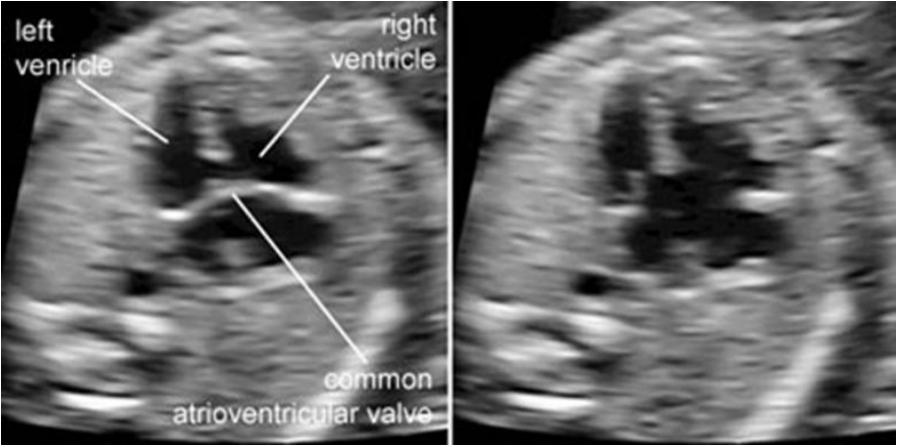
Salient features:
- Single atrioventricular valve draining both atrium into respective ventricle
- Generally regurgitating commoc AV avlve
- Primum atrial septal defect and Inlet ventricular septal defect
- Associated with: Down’s , isomerism, DORV.
Ebstein anomaly
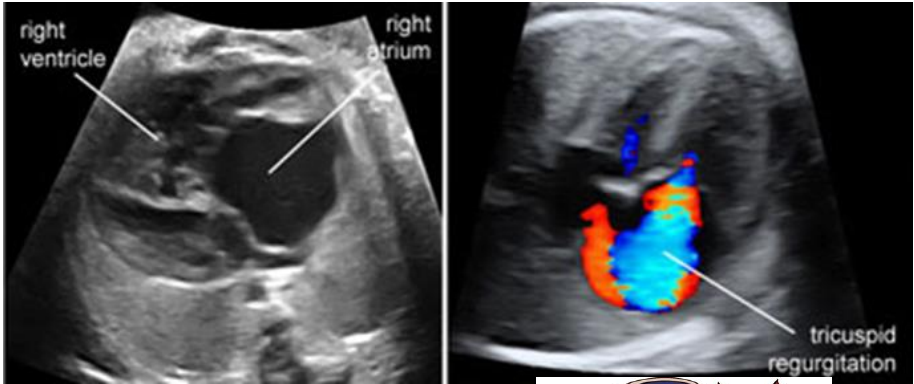
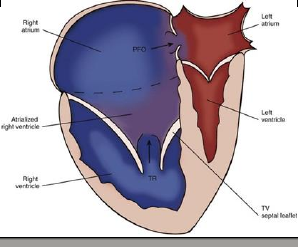
Salient feature
- Hugely dilated RA and RV
- Few of the largest heart: High cardio thoracic ratio
- Severe TR
- May have functional pulmonary atresia
- Larger the RA , worse the prognosis
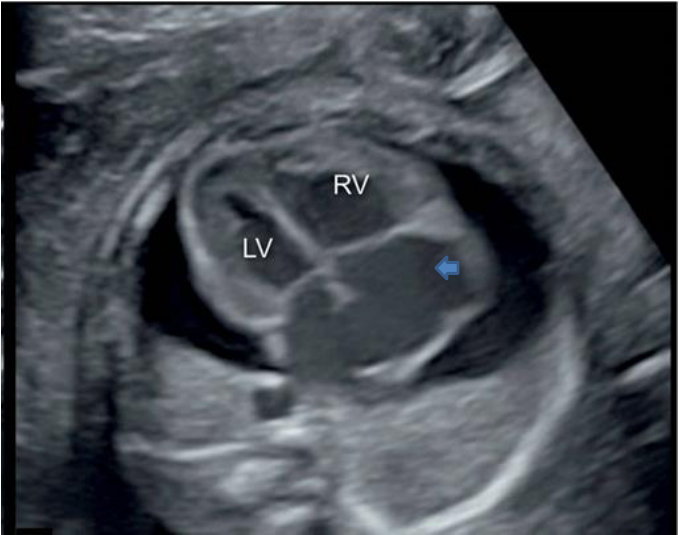
Ventricular septal defect
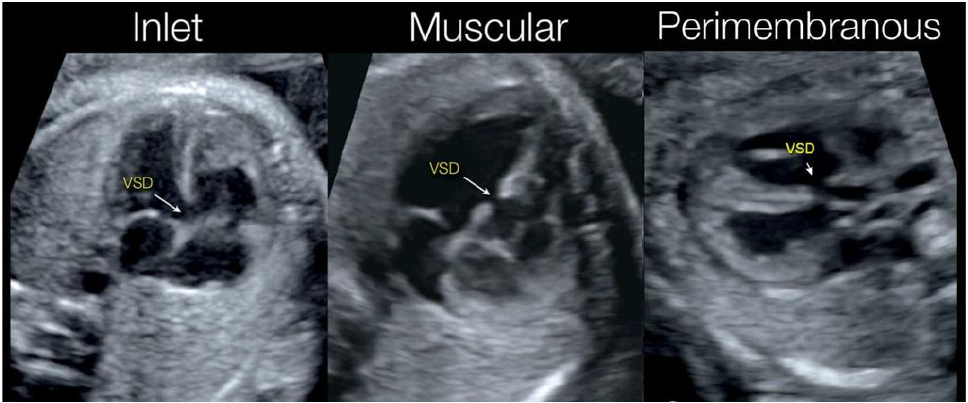
- Most challenging diagnosis
- Mere presence of septal dropout is not diagnostic
- Look for hyper echoic margin
- Verities: Perimembranous / inlet/ muscular/
- outlet
- Perimembranous most common
- Vey large VSD can behave as single ventricle
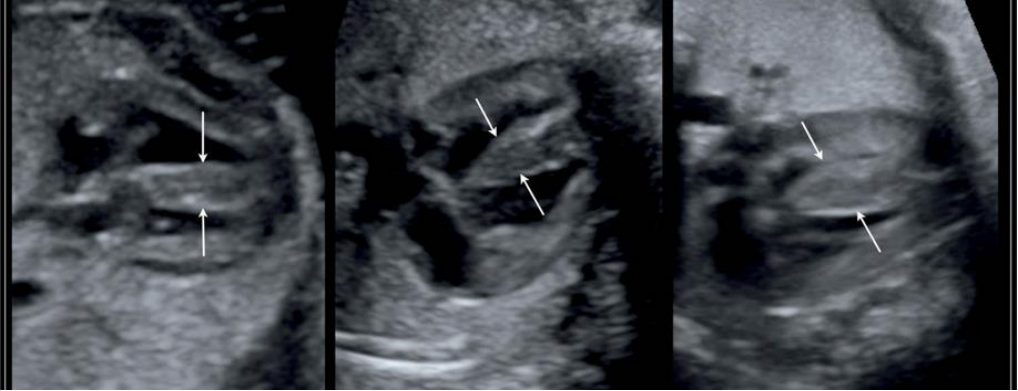
Congenitally corrected transposition
of great arteries
- In either situs, morphological atria at normal position
- Morphological right ventricle is more posterior and
- leftward (RV) ( Solitus)
- Morphological Left ventricle is more anterior and
- rightward
- Cardiac axis can be anteroposterior ( mesocardia)
- Left sided AV valve is more apical (Tricuspid valve
- Arrow) than right sided valve ( Mitral valve Arrow
- head)
- Chances of AV block
Dilated cardiomyopathy
cardio
thoracic
ratio
Salient features:
- Cause: Maternal lupus, infective myocarditis, tachy arrhythmias, AV blocks, genetic/ inherited
- Dilated ventricles with decreased contractility
- Increased cardio thoracic ratio
- Features of hydrops fetalis
- IUGR and IUFD quite common
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Salient features:
- Causes: Diabetic mother, Noonan syndrome, Glycogen storage disease, Hereditary ( HCM)
- Can present anytime from utero to 20 years
- Excessively thick myocardium ( check ‘z’ score for gestational age )
- May be localized to IVS or generalized
- Risk of IUGR and IUFD
- Generally hereditary
- Storage disorders
Pericardial effusion
Salient features:
- Generally secondary to hydrops fetalies, Down’s syndrome, chromosomal anomalies
- There is free fluid around heart.
- Mild to moderate effusion will improve, however large ones
- need special attention.
Cardiac masses
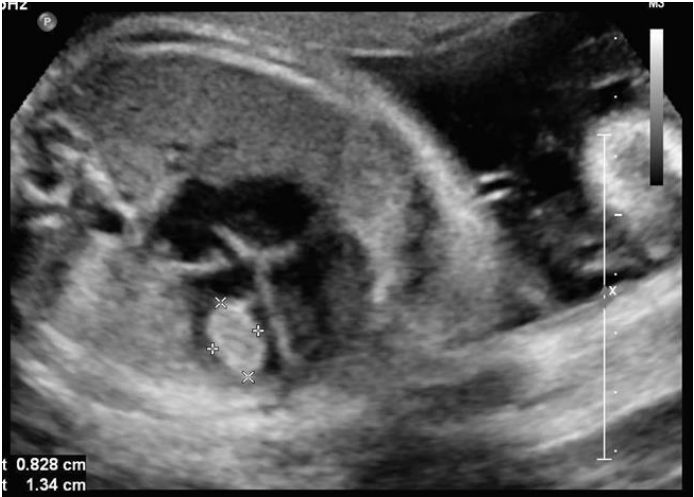
- Causes: Rhabdomyoma, teratoma, fibroma, hemangioma,
- Rhabdomyoma: Tuberous sclerosis, multiple, intra myocardial affecting ventricles, rhythm disturbances. Regress spontaneously.
- Teratoma: Intra pericardial with effusion, mainly Rt side, near aortic / pulmonary root,
- Can cause obstructive symptoms.
Anomalies seen on 4 chamber view: which don’t have 4 chambered heart.
- One of the ventricle along with AV valve is very small or absent.
- These defects require multistage palliative surgical correction ( single ventricle repair).
- They may be associated with outlet defect like aortic/ pulmonary stenosis/ atresia, TGA, DORV etc.
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
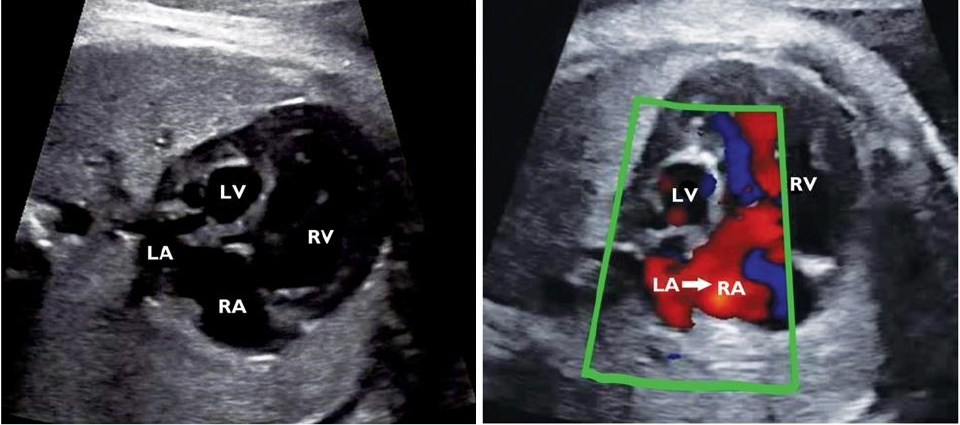
Hypoplastic left ventricle
Salient features:
- Left ventricle : small size, not reaching up to apex, sometimes may be absent
- Mitral andaortic valve : small / stenosis/ atretic
- Flow reversal in oval foramen and distal aortic arch is characteristic.
- Endocardial fibroelastosis of left ventricle
- One of the most challenging heart defect to treat.
- Quite common
Hypoplastic right heart PA IVS
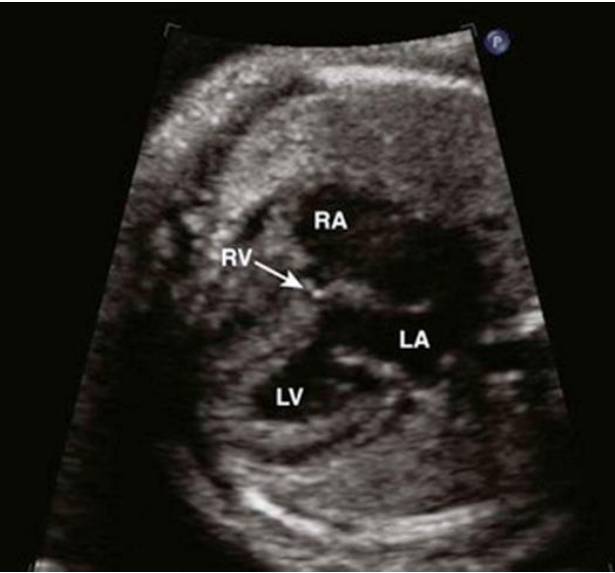
Salient features:
- Right ventricle: small, not apex forming. May be absent
- Tricuspid Valve: if present, it is at normal position. Generally hypoplastic , dysmorphic or atretic , frequently severe TR with dilated RA
- Pulmonary valve: Atretic.
- Flow reversal in PDA ( PDA dependent pulmonary circulation)
- Challenging disease to treat.
Tricuspid atresia
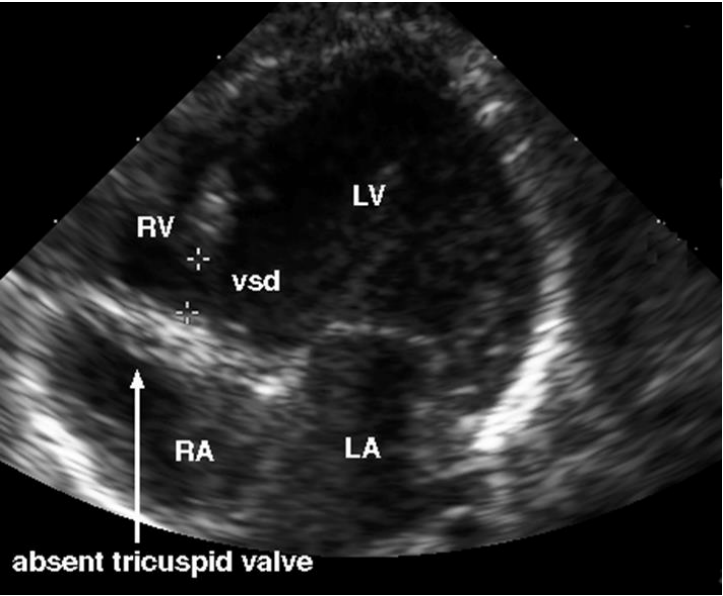
Salient feature
- Tricuspid valve: atretic/ not formed. No forward flow across the valve.
- Right ventricle: Usually very small
- VSD : generally present
- Pulmonary valve: May be normal/ small / atretic
- Mitral valve and left ventricle: Dominant
- Great arteries: Normal/ trans position/ other combinations possible.
Mitral atresia
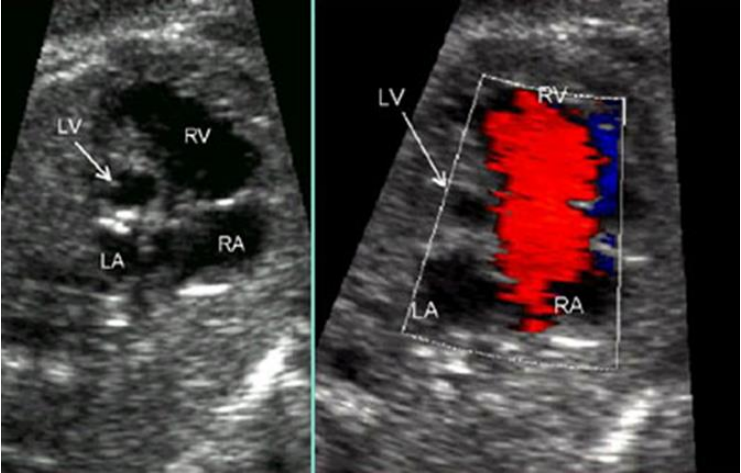
Salient features
- Mitral valve not formed, no forward flow
- Left ventricle: usually small or absent
- Aortic valve: Small / absent/ from RV
- VSD : may be present
- Oval foramen : flow reversal
- Tricuspid valve and RV dominant:
- Flow reversal in distal aortic arch may be present
Double inlet ventricle / single ventricle
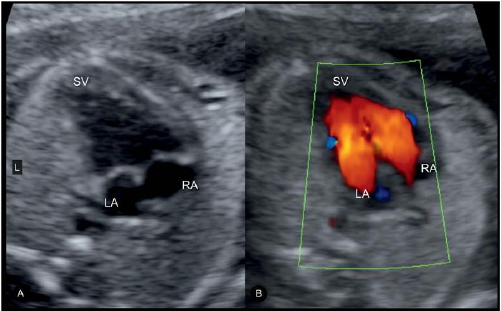
Salient feature
- Inter ventricular septum : very large VSD, absent or abnormal deviation to one side
- LV is generally dominant
- Both atria drain into single ventricle through two or one AV valve
- AV valves may be normal/ common/ atresia of one AV valve
- Great vessels: Pulmonary artery from main ventricle/ Aorta from outlet chamber or vice versa. Many possibilities.
Anomalies seen on 4 chamber view: A not so normal 4 chamber view
- These lesions include are sitting on fence of above 2 categories. GREY ZONE.
- On of the ventricle is smaller than usual with possibility that it can function independently.
- Careful evaluation of all parameters will help to decide management plan.
- Close follow up during gestation generally helpful.
Unequal sizes of ventricle
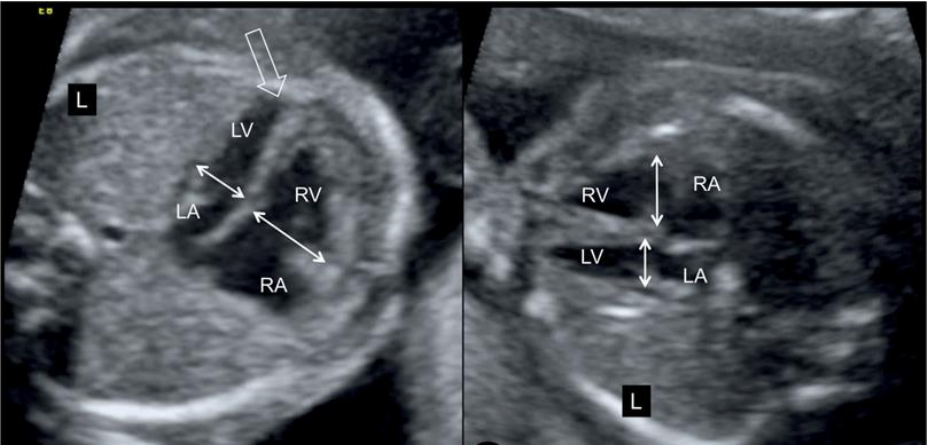
- LV or RV smaller for gestational age ( second trimester)
- Always check for Z score of mitral, tricuspid, aortic and pulmonary valve, long and short diameter of LV, aortic arch, isthmus, pulmonary artery.
- Indirect evidence for coarctation / aortic arch interruption/ TAPVC / PA IVS/ HLHS.
- Aortic arch may be difficult to see
Endocardial fibroelastosis
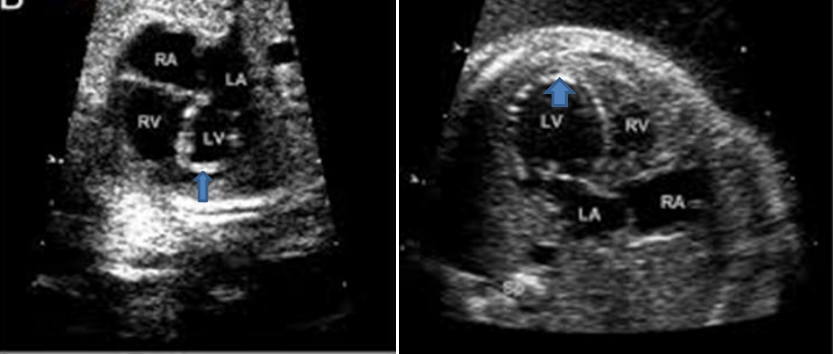
Salient feature:
- Endocardial border hyperechoic
- Associated with LV systolic as well as diastolic dysfunction Common associated lesions: Aortic stenosis/ hypoplastic left heart syndrome/ viral myocarditis/ autoimmune / Autosomal or X linked
- Leads to hydrops fetalis , IUGR/ IUFD

REPLY COMMENT