What are trans catheter cardiac interventions? (TCC)
Trans catheter cardiac intervention is a specialized procedure in which a long, flexible tube—a catheter—is inserted into a vein or artery and guided into the heart. The procedure is very much similar to angiography done in adults.
Congenital heart defects are treated with surgery for more than 60 years. Invention of new materials and modern technology have opened a new avenue of TCC in last 30 years where we can correct certain defects without scalpel, scissors, stitches and the most important no scar marks.Paediatric cardiologist is specially trained in TCC of infants and children. Decision to perform TCC or surgery is taken after detail 2D echo cardiography examination ( Neonatal and Pediatric 2D echocardiography). Cardiologist will guide you after going through the report.
Some common defects where TCC is frequently used:
- Valvuloplasty of cardiac valves: Some time heart valves are deformed and do not open adequately resulting into obstruction to blood flow. Balloon dilatation of these valves makes them roomy and relieves obstruction
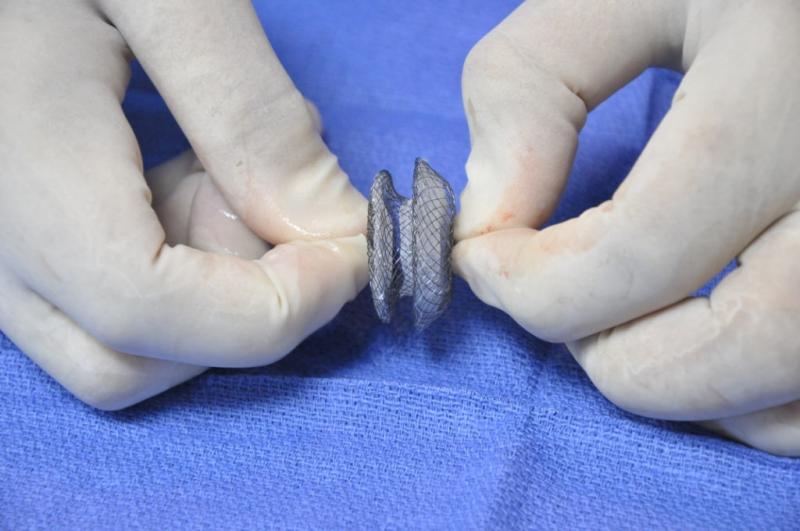
- Closure of holes in heart: Partitions in heart can have holes. They can be closed effectively with help of umbrella shaped devices. This devices patch the hole and prevent blood flow. ( Atrial septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect, )
- Abnormal connection between artery and vein ( AV malformations): These connections can be closed with the help of plugs. They are generally present in lung.
- To open atrial septum immediately after birth in cyanotic heart defects with balloon.
- Dilate stenotic blood vessels: With help of balloons and stents ( scaffold of wire) narrowed blood vessel can be dilated. (Coarctation of aorta, pulmonary artery stenosis)
- Cardiac biopsy: Just like any biopsy heart tissue can be obtained with catheterization
- Diagnostic catheterization: Sometimes information obtained by non-invasive means (echocardiography) is inadequate which can be gathered by catheterization.
- Electrophysiology study: This is used to ablate abnormal electrical connection in heart.
Can all heart defects be fixed with TCC?
Selected heart defects like atrial septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus, ventricular septal defects, aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis, AV malformation, coarctation etc can be fixed with TCC. Echocardiography examination generally gives answer to this question. Most of the complex defects like TOF, TGA can be treated only with surgery.
After corrective surgery, a definite percentage of patients develop new problems like peripheral pulmonary stenosis, re-coarctation, severe pulmonary regurgitation, conduit stenosis etc. They can be effectively fixed with TCC (post cardiac surgery care).
Consult doctor
What are the advantages of TCC over open heart surgery when both options are suitable?
All the defects treated with TCC can be also treated with surgery but there are some advantages of TCC over surgery
- As there is no need to open chest, there is no scar, no pain after intervention.
- Patient enjoys faster recovery after TCC and can resume routine activity within a day or two.
- As cardiopulmonary bypass is not required, there are no complication related to same.
- Long term results of TCC are as good as surgery and sometimes better.
How my child will undergo TCC?
TCC is performed by specially trained paediatric cardiologist. If your child needs TCC, he will asses him/her and study all relevant report. You will be explained about nature of procedure, need, success, alternative therapies, duration of stay, preparation and complications also. He will obtain consent from parent/ guardian in case of a minor. An appointment will be given to you. Most catheterization require hospitalization for 2 to 3 days. Some procedures can be planned on day care basis.
TCC is performed in catheterization laboratory with the help of X ray also called as fluoroscopy. A specialised and trained team of nurses and technicians assist cardiologist during procedure. Vitals of baby are continuously monitored by dedicated monitors. The team see to it that the baby is comfortable during procedure.
Important steps in TCC
Step 1)The child will be given sedation so he/she sleeps. Some times general anaesthesia is used. Site of catheter insertion is cleaned with antiseptic solution to make it free of germs. Local anaesthetic agent is injected below skin so pain is not felt. Generally groin vessels are used.
Step 2)With help of needle paediatric cardiologist enters into vein or artery. Under fluoroscopy guidance, with help of wires, he advances catheter into heart. He studies following thing: a)The course of catheter into different chambers, b)blood pressure and oxygen content in chambers of heart and blood vessels, c)Sometimes with help of contrast agent he studies anatomy of blood vessels. Blood samples are drawn from various sites. This data give information about heart function, circulation in lungs and body, obstruction to blood flow etc.
Step 3) Therapeutic procedure like device closure of hole , balloon dilatation of small valves etc are done in same setting.
Recovery:
After procedure is over, catheters are withdrawn from body. Haemostasis is achieved at the of entry point with help of pressure and bandage so that there is no bleeding. Vital parameters are assessed and the kid is shifted to recovery . He/she will be observed for several hours by intensivist and trained nurses. Legs from which catheter was introduced is kept immobilised to prevent re-bleeding.
Results of procedure:
Paediatric cardiologist will discuss results of catheterization with you in detail. He will guide you about present condition, success of procedure, nature of treatment required, plan for the child.
Discharge:
You will receive written instructions about care of the catheterization site, bathing, activity, restrictions and any new medications your child may need to take at home. Generally baby will have mild discomfort at puncture site, which will improve in a few days.


REPLY COMMENT