Before you begin reading about transposition of the great arteries, please read the explanation of how the normal heart works for a basic understanding of its structure and function.
- What is transposition of the great arteries?
- What are the symptoms of TGA?
- How is TGA diagnosed?
- What are the treatment options for TGA?
- What kind of follow-up care is required for TGA?
What is transposition of the great arteries (TGA)?
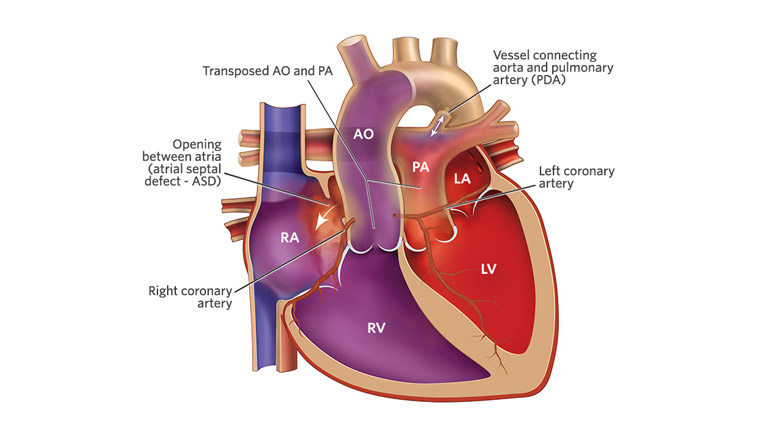
In simple words, it is interchange in position of aorta and pulmonary artery:- the two large (great) arteries carrying blood from heart to body and lungs respectively. As a result, the change in blood circulation is as follows:
- The aorta is attached to the right ventricle (pumping chamber), instead of the left. Right side of heart receives impure blood and it is pumped into aorta. As a result blood (impure/de-oxygenated) returning from body goes back to body instead of going to lungs.
- The pulmonary artery is attached to the left ventricle (pumping chamber), instead of the right. Left side of heart receives pure/ oxygenated blood from lungs and it is pumped into pulmonary artery. As result blood (pure) returning from lungs goes back to lungs instead to going to body.
Which defects are associated with TGA?
- Patent formen ovale: It is communication between atria ( upper chamber)
- Patent ductus arteriosus: It is communication between aorta and pulmonary artery.
- Ventricular septal defect: Hole in partition between lower chambers (ventricles)
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Other rare anomalies: Coarctation, atioventricular valve defets
These 2 defects are necessary for survival immediately after birth as they allow mixing of blood and body gets more oxygenated blood.
What are the symptoms of TGA?
Symptoms of TGA result from supply of impure/ de-oxygenated blood to body:
- Blue or purple discoloration of lips, skin and nails (cyanosis)
- Rapid breathing
- Difficulty feeding; poor appetite and poor weight gain
How is transposition of the great arteries diagnosed?
TGA is a frequently missed in neonates. Paediatrician of neonatologist would pick it up on the basis of symptoms
- Fetal echocardiography: DORV is diagnosed before birth with fetal echocardiogram (ultrasound). If we have pre-hand knowledge of disorder we can plan deliver in a well equipped centre and start care immediately after birth.
- Echocardiogram – It gives accurate information about defect in heart.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – a record of the electrical activity of the heart
- Chest X-ray
- Pulse oximetry – It is a very important but simple test to suspect TGA soon after birth.
- Cardiac catheterization
- Cardiac MRI
What are the treatment options for TGA?
Initial stabilization: Approximately one-third of newborns with TGA have extremely low oxygen levels in blood that can harm their bodies. They require an urgent intervention, called a balloon atrial septostomy (BAS), within hours after birth. This is a life-saving procedure. With help of a balloon a hole between the upper chambers of the heart is created or enlarged. It allows pure and impure blood mix and increases supply of oxygenated blood to body. Medicines are given to keep ductus arteriosus open which helps further.
All children with TGA will require open-heart surgery to treat the defect. Without surgical repair, the overwhelming majority of patients with TGA will not survive their first year.There are 2 ways of corrction
Arterial switch opration:
The surgery is typically performed within a few days of birth. Surgeons reconstruct the heart so that the aorta which is originally attached to right ventricle is re-attached to the left ventricle and the pulmonary artery which is originally attached to left ventricle is re-attached to the right ventricle. Coronaries are also moved along with aorta.
Atrial switch (Mustard/Sanning):
In some cases, connections of atria to ventricle are reversed. Left atrium is attached to right ventricle and right trium is connected to left ventricle.
After both corrections mentioned above, circulation is maintained like a normal heart. Body gets oxygenated blood from lung and lungs gets de-oxygenated blood from body.
Does surgery gives cure to my child? Do I need to follow up?
Surgical correction has revolutionized life of children with TGA. After correction these kids live a pretty normal life, they attain school, participate in sports, they grow as an responsible adult.
All Children who have had surgical repair of TGA require life-long care by a paediatric cardiologist. There is a chance of narrowing of blood vessels at site of suturing. Left pulmonary artery is particularly prone for narrowing. Mild narrowing is well tolerated while severe narrowing needs surgical correction or balloon dilatation. As pulmonary valve functions at aortic position, it can develop leak over period time.
Atrial switch is not practiced routinely now. It was a standard procedure 25 years back. These babies used to develop atrial arrhythmia and dysfunction of ventricle.

REPLY COMMENT